Understanding the Effects of Thumb Sucking
Introduction
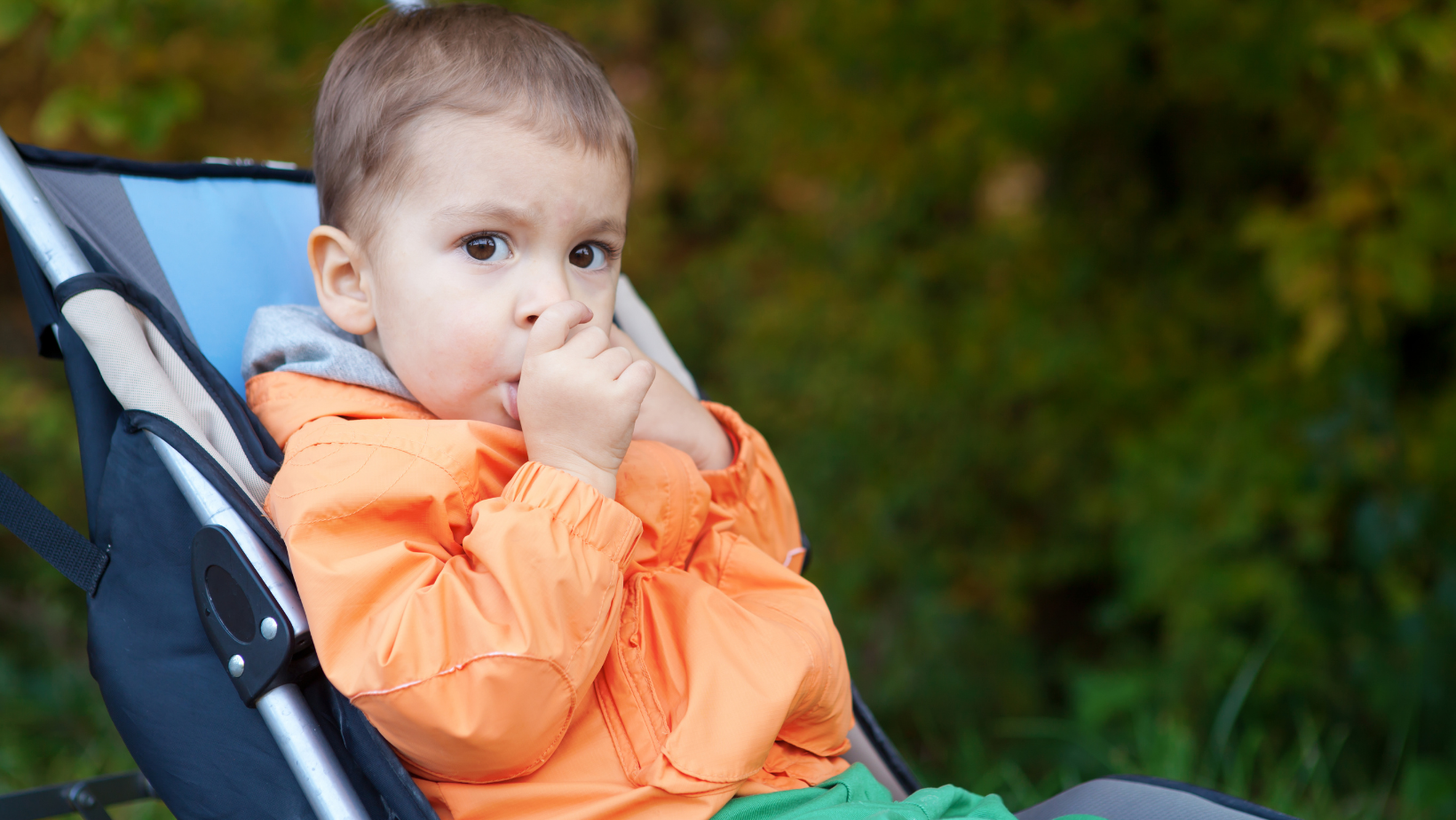
Thumb sucking is a natural reflex for infants and toddlers, serving as a source of comfort and security during their early years of development. While it is a common and often harmless habit in the initial stages of childhood, prolonged thumb sucking can have significant implications on a child’s dental and facial development. Understanding these effects is crucial for parents and caregivers to ensure that children transition out of this habit at an appropriate time, safeguarding their overall oral health and well-being.
Why Do Children Suck Their Thumbs?
The Psychological and Comfort Aspects of Thumb Sucking
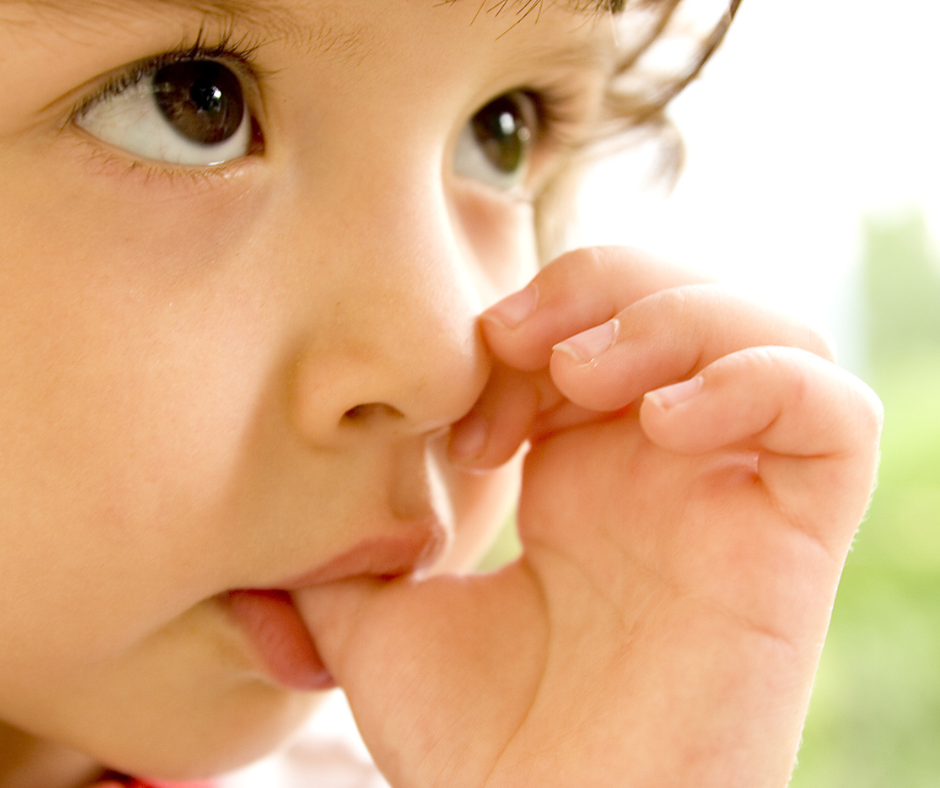
Thumb sucking is not merely a physical action but a comforting behavior that helps children cope with stress, anxiety, or boredom. For many infants, it’s an instinctive method of self-soothing that helps them feel secure and happy. This behavior is especially prevalent during the first few years of life, often used as a mechanism to fall asleep or navigate through new and challenging situations. While thumb sucking is a normal part of development, its continuation beyond the preschool years can begin to impact a child’s oral health significantly.
Negative Effects of Thumb Sucking on Dental Health
Impact on Teeth Alignment and Jaw Development
Prolonged thumb sucking can exert pressure on the teeth, jawbone, and soft tissue in the mouth, leading to several orthodontic issues. The constant presence of a thumb in the mouth can cause the upper front teeth to push outwards and the lower front teeth to tilt inwards, resulting in malocclusion or misalignment of the teeth. Additionally, this habit can lead to alterations in the roof of the mouth and affect normal jaw growth, potentially necessitating orthodontic treatment later in life to correct these abnormalities.
Risk of Developing Speech Issues
Beyond its impact on dental structure, thumb sucking can also influence speech development. The habit may lead to problems such as lisping or the inability to pronounce certain sounds correctly. This is because the natural resting position of the tongue is altered, affecting its movement and, consequently, the production of speech sounds. Children who suck their thumbs for an extended period are at a higher risk of developing speech impediments, emphasizing the importance of addressing this habit early on.
The effects of thumb sucking on dental health highlight the need for awareness and intervention when necessary. By understanding the potential consequences and taking proactive measures, parents can help ensure their children’s oral development remains on track, paving the way for healthy teeth and proper speech development.
When Should Thumb Sucking Be a Concern?
Age Considerations and Dental Health
Thumb sucking is a natural reflex that most children outgrow by the age of 4 to 5. However, if the habit persists beyond this age, especially once permanent teeth begin to emerge, it may start to pose risks to dental health. The prolonged pressure of thumb sucking can lead to misaligned teeth and changes in jaw structure, necessitating orthodontic intervention. Monitoring this habit as children grow is essential; early detection and intervention can mitigate potential dental issues and contribute to healthier oral development.
Strategies for Mitigating the Effects of Thumb Sucking
Tips for Parents to Discourage Thumb Sucking
Encouraging a child to stop thumb sucking involves patience, understanding, and support. Here are some practical strategies for parents:
- Positive Reinforcement: Praise and reward your child for not sucking their thumb, emphasizing their growth and maturity.
- Identify Triggers: Understand what prompts your child to suck their thumb, whether it’s stress or boredom, and offer alternatives to comfort them.
- Use Reminders: A small bandage on the thumb or a sock on the hand at night can serve as gentle reminders.
- Create a Support System: Encourage siblings and family members to support the child in overcoming the habit without shaming.
When to Seek Professional Advice
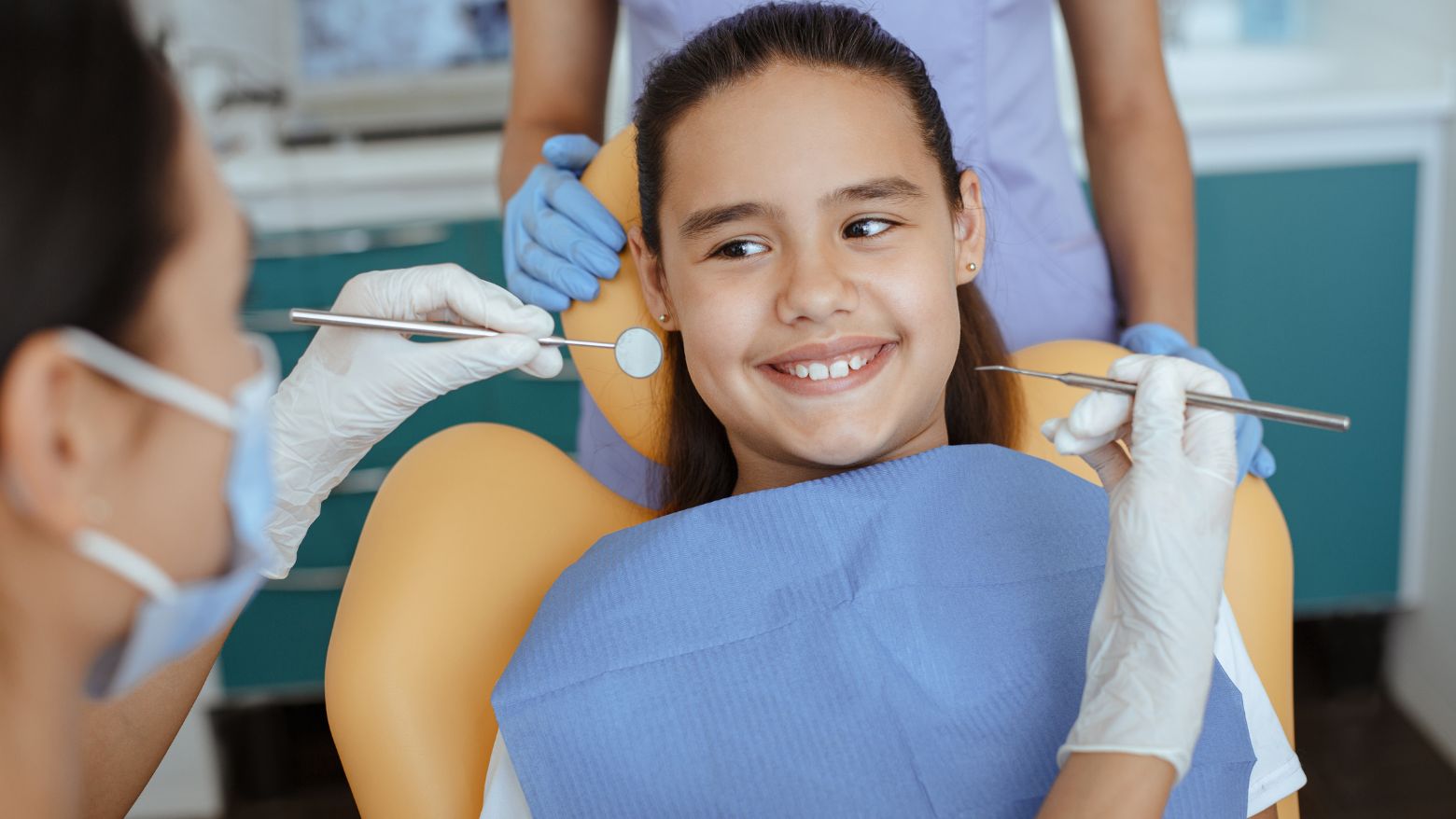
If thumb sucking persists beyond the age when permanent teeth are starting to appear, it’s wise to consult a pediatric dentist or orthodontist. Indications for seeking professional advice include noticeable changes in the child’s teeth alignment, jaw structure, or if the child experiences anxiety about the habit. Dental professionals can offer tailored strategies, including appliances to discourage thumb sucking, and provide guidance on protecting your child’s dental health.
The Role of Pediatric Dental Care in Managing Thumb Sucking Effects
Preventive Measures and Early Intervention
Regular dental check-ups play a pivotal role in the early detection of any adverse effects of thumb sucking on dental development. Pediatric dentists can monitor changes in teeth alignment and jaw growth, offering preventive advice and interventions when necessary. Early intervention may include the use of dental appliances to discourage thumb sucking and guidance on behavioral strategies to help children break the habit. Establishing a relationship with a pediatric dental care provider ensures that children receive the support and care needed to address thumb sucking effectively, safeguarding their oral health and contributing to their overall development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: At what age does thumb sucking become a concern for dental development?
A1: Thumb sucking becomes a concern if it continues beyond the age of 4 to 5 years, especially as permanent teeth start to emerge, as it can lead to dental misalignments.
Q2: Can thumb sucking affect my child’s speech?
A2: Yes, prolonged thumb sucking can lead to speech issues, such as lisping or difficulty pronouncing certain sounds, due to alterations in the position and function of the tongue.
Q3: What are some effective strategies to help my child stop thumb sucking?
A3: Effective strategies include positive reinforcement, identifying and addressing triggers, gentle reminders like bandages or socks, and seeking professional advice if needed.
Q4: When should I seek professional help for my child’s thumb-sucking habit?
A4: It’s advisable to consult a pediatric dentist or orthodontist if the habit persists beyond the age when permanent teeth appear, or if there are noticeable effects on dental alignment or speech.
Q5: Are there any dental devices that can help stop thumb sucking?
A5: Yes, dental professionals can recommend appliances that fit in the mouth and obstruct thumb sucking, serving as a physical barrier and helping to break the habit over time.
The Psychological Impact of Thumb Sucking in Children
Understanding Emotional Connections
Thumb sucking in children is not just a physical habit but often a manifestation of seeking comfort and security. This behavior is deeply rooted in the psychological need for soothing, particularly during the early stages of development when children are beginning to navigate the world around them. The emotional connection to thumb sucking can be strong, making it a challenging habit to break. Recognizing this aspect is crucial for parents and caregivers as they guide their children through the process of discontinuing the habit. Approaching the situation with empathy and understanding, rather than punishment or shaming, is key to successfully addressing the emotional needs underlying thumb sucking.
The Role of Family Support in Overcoming Thumb Sucking
Fostering a Supportive Environment
The journey to break the habit of thumb sucking is greatly influenced by the support system around the child. Family members play a pivotal role in providing a nurturing and encouraging environment that motivates the child to give up thumb sucking. Sharing stories of others who have successfully overcome the habit, engaging in family activities that keep the child’s hands busy, and collectively celebrating milestones of progress can reinforce a child’s motivation to stop. A supportive family environment ensures that the child does not feel isolated or criticized for their habit, making the transition smoother and more effective.
Long-Term Dental Health: Beyond Thumb Sucking
Emphasizing Preventive Care
While addressing thumb sucking is important for preventing dental misalignments and promoting proper oral development, it’s also a gateway to broader discussions on long-term dental health. Educating children on the importance of regular dental hygiene practices, such as brushing, flossing, and routine dental check-ups, can instill habits that contribute to lifelong dental health. For children who have engaged in prolonged thumb sucking, early and consistent dental care becomes even more critical to monitor their development and address any issues promptly. Emphasizing preventive care and healthy oral habits from an early age sets the foundation for strong, healthy teeth well into adulthood.